A Comprehensive Guide to Life Insurance: Benefits, Types, and How It Works
Life insurance is a contract between an individual (the policyholder) and an insurance company, where the insurer promises to pay a designated beneficiary a sum of money upon the death of the insured person. Life insurance offers financial security and peace of mind for both the policyholder and their loved ones. This guide will explain the benefits of life insurance, the types available, and essential considerations when purchasing a policy.
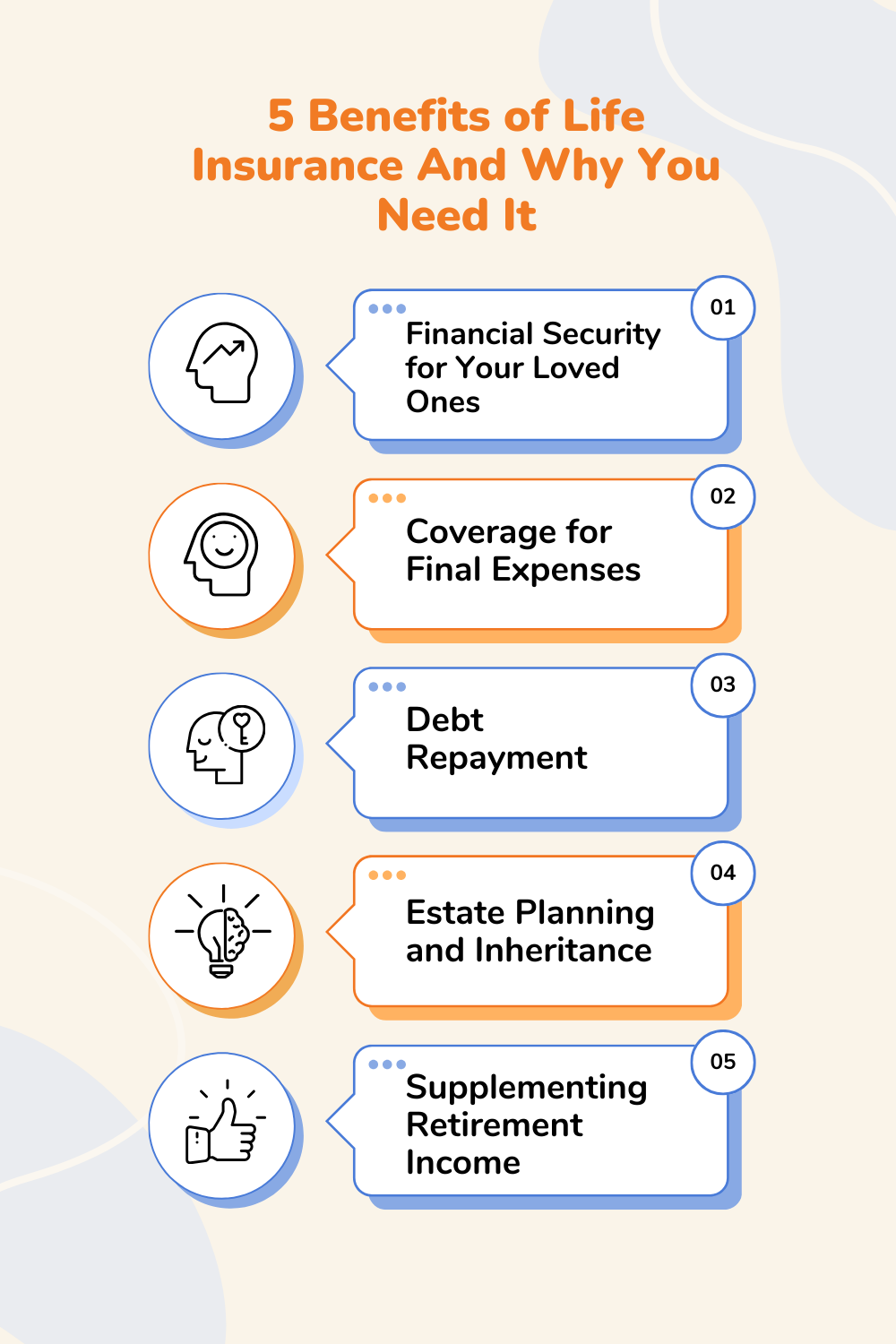
Top 5 Benefits of Life Insurance
- Financial Security for Your Loved Ones
Life insurance provides a safety net for your dependents, ensuring they can maintain their standard of living in your absence. This financial cushion can help cover daily expenses, mortgage payments, education costs, and even healthcare bills. It protects your family from financial hardship after you’re gone. - Coverage for Final Expenses
Funerals, burial or cremation services, and related expenses can be costly, often ranging from $5,000 to $15,000 or more. A life insurance policy can cover these final expenses, ensuring that your family doesn’t have to bear the burden of paying for funeral costs during an emotionally difficult time. - Debt Repayment
If you have outstanding debts such as mortgages, car loans, or personal loans, life insurance can ensure that these obligations are settled after your death. This benefit prevents your family members from inheriting your debt, allowing them to maintain financial stability without worrying about repaying creditors. - Estate Planning and Inheritance
Life insurance can play a key role in estate planning, allowing you to leave a financial legacy to your heirs. A life insurance policy can provide your beneficiaries with a lump sum of tax-free money, helping to equalize inheritance distributions or ensure that specific family members receive a designated amount. - Supplementing Retirement Income
Certain types of life insurance, particularly permanent policies like whole life or universal life, can accumulate cash value over time. You can borrow against or withdraw from this cash value to supplement your retirement income or cover other financial needs during your lifetime.
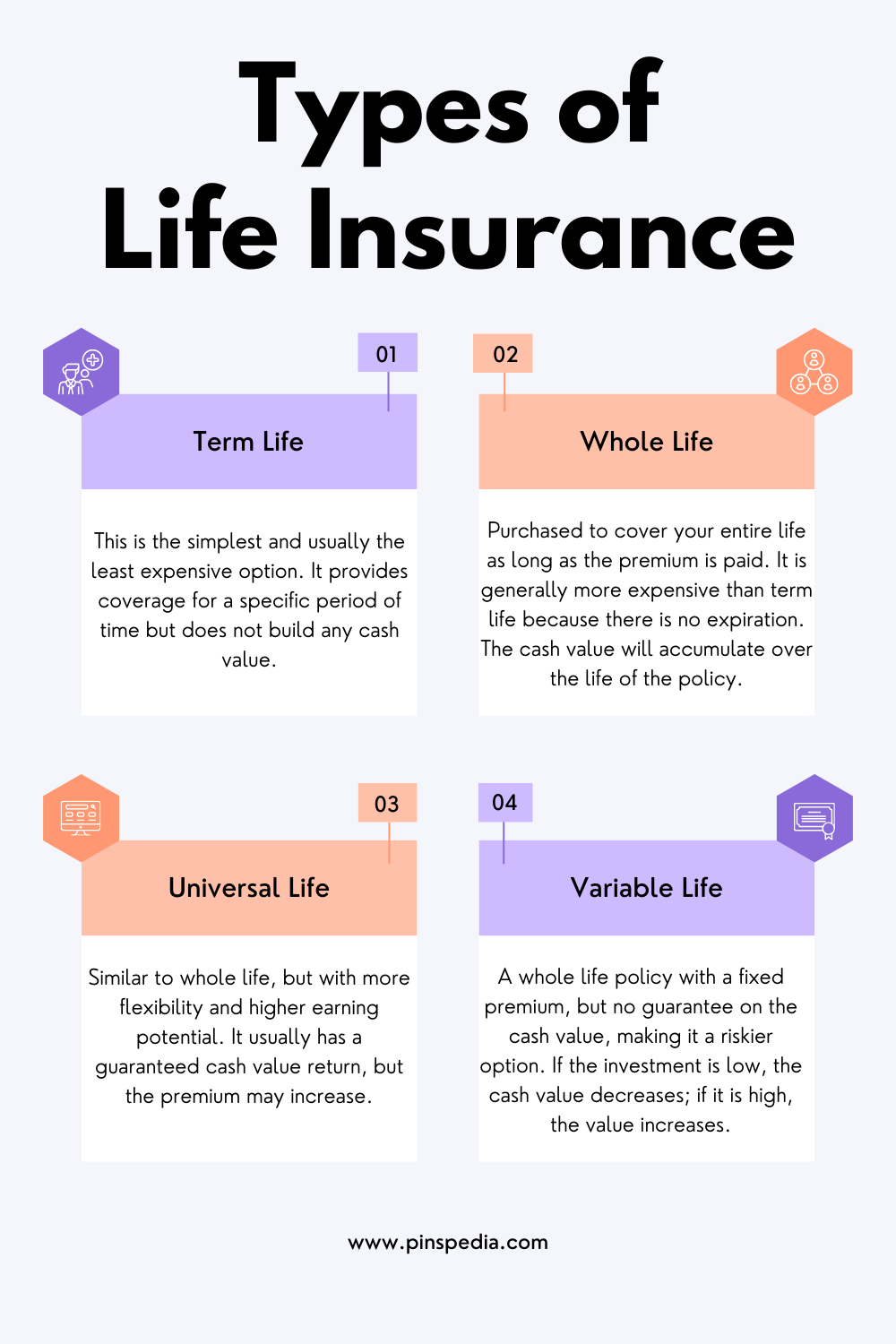
Types of Life Insurance
Life insurance comes in several forms, each with its unique features and benefits. The most common types include:
1. Term Life Insurance
- How it works: Term life insurance provides coverage for a specified period, such as 10, 20, or 30 years. If the insured dies during the term, the beneficiaries receive the death benefit. If the policyholder outlives the term, no payout is made unless the policy is renewed.
- Best for: Those seeking affordable coverage for a specific period, such as during child-rearing years or while paying off a mortgage.
- Pros: Lower premiums, simple to understand, provides coverage when it’s most needed.
- Cons: No cash value or savings component, and coverage ends when the term expires.
2. Whole Life Insurance
- How it works: Whole life insurance offers coverage for the policyholder’s entire life, as long as premiums are paid. It also includes a savings component (cash value) that grows over time and can be borrowed against or withdrawn.
- Best for: Individuals looking for lifelong coverage and a policy that builds cash value.
- Pros: Lifetime coverage, guaranteed death benefit, and cash value accumulation.
- Cons: Higher premiums compared to term life, and cash value growth may be slower than other investments.
3. Universal Life Insurance
- How it works: Universal life insurance is a flexible type of permanent insurance that allows policyholders to adjust their premium payments and death benefit. It also includes a cash value component that grows based on interest rates.
- Best for: Individuals who want flexibility in premium payments and death benefits, and are looking for an investment component with their insurance.
- Pros: Flexibility in payments, potential for cash value growth based on interest rates.
- Cons: Complex structure, cash value dependent on interest rates, which could affect policy performance.
4. Variable Life Insurance
- How it works: Variable life insurance allows policyholders to invest the cash value portion in various investment options such as stocks and bonds. The death benefit and cash value fluctuate based on the performance of the investments.
- Best for: Individuals with a higher risk tolerance who want investment growth potential within their life insurance policy.
- Pros: Potential for higher returns based on investments, lifelong coverage.
- Cons: Investment risk, higher fees, complex structure, and potential for policy lapsing if investments underperform.
5. Final Expense Insurance
- How it works: Also known as burial or funeral insurance, final expense insurance is a type of permanent life insurance designed to cover end-of-life expenses, such as funeral costs, medical bills, or unpaid debts.
- Best for: Seniors or those looking for an affordable way to cover final expenses.
- Pros: Lower premiums, specifically designed to cover final costs.
- Cons: Lower death benefits, typically between $5,000 and $25,000, limited in scope.
How Life Insurance Works
- Choosing a Policy
- Determine the amount of coverage you need. This depends on factors like your income, outstanding debts, future financial obligations (e.g., education costs), and your family’s financial needs.
- Select the type of life insurance that best fits your needs and financial goals. For temporary coverage, term life insurance may suffice. For lifelong protection with added savings or investment options, a permanent policy may be more appropriate.
- Paying Premiums
- Life insurance policies require regular premium payments, which can be monthly, quarterly, or annually. If you stop paying premiums, the policy may lapse, and you could lose coverage. For term policies, premiums typically remain level throughout the term, while permanent policies may have flexible payment structures.
- The Death Benefit
- When the insured person passes away, the insurance company pays the death benefit to the beneficiaries listed on the policy. This payout is generally tax-free and can be used by the beneficiaries for any purpose, such as covering living expenses, paying off debts, or saving for the future.
- Cash Value (for Permanent Policies)
- For whole life, universal life, and variable life policies, a portion of the premiums goes toward building cash value. This cash value grows over time and can be accessed through loans or withdrawals while the policyholder is alive. However, borrowing from the cash value reduces the death benefit unless repaid.
Key Considerations When Buying Life Insurance
- Assess Your Financial Needs: Consider your current income, debts, and family needs to estimate how much life insurance coverage you require.
- Compare Policies: Review different types of policies and get quotes from multiple insurers to find the best policy for your budget and needs.
- Understand the Terms: Ensure you know the policy’s terms, including premium payments, death benefits, and how the policy works over time.
- Check the Insurer’s Reputation: Choose a reputable and financially stable insurance company with a good track record of paying out claims.
Conclusion
Life insurance is a crucial tool for financial planning, providing protection and peace of mind for you and your loved ones. Whether you’re looking to secure your family’s financial future, cover final expenses, or leave an inheritance, there’s a policy to fit your needs. By understanding the different types of life insurance and their benefits, you can make an informed decision that ensures your family is protected long after you’re gone.