Types of Life Insurance
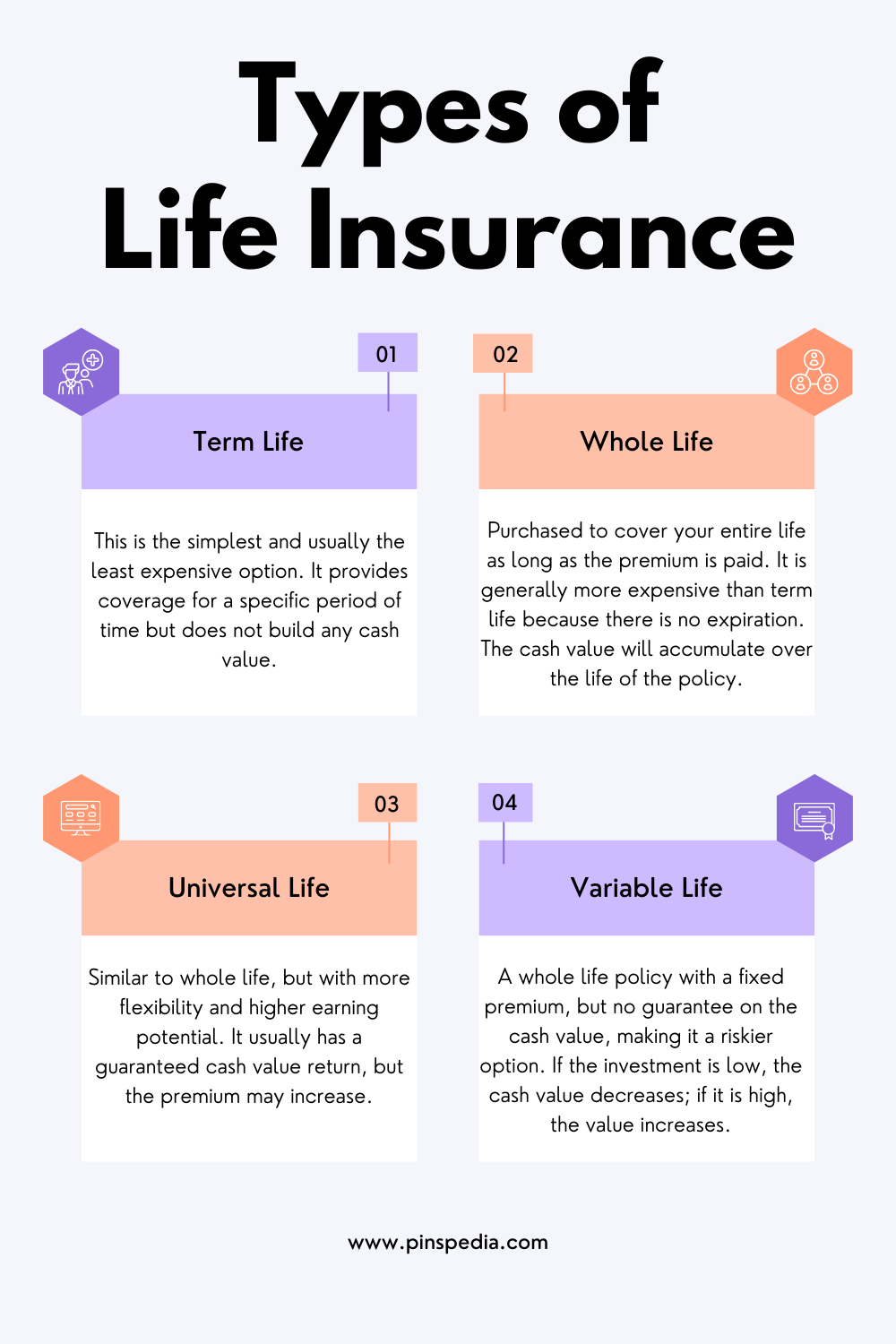

Life insurance is a critical part of financial planning, ensuring that your loved ones are financially protected in the event of your death. It provides a safety net, helping to cover debts, funeral costs, or ongoing living expenses for your dependents. But with several types of life insurance available, it can be difficult to choose the one that best suits your needs. This article will explore the four primary types of life insurance—Term Life, Whole Life, Universal Life, and Variable Life—to help you make a more informed decision.
1. Term Life Insurance
Term life insurance is often considered the simplest and most affordable option, making it an attractive choice for many individuals. As the name suggests, this type of policy provides coverage for a specific period of time, known as the “term,” which can range from 10, 20, or even 30 years. The main objective of term life insurance is to offer a death benefit to your beneficiaries if you pass away during the policy’s term.
Key Features:
- Affordability: One of the primary reasons people opt for term life insurance is its affordability. Since it does not include a savings or investment component, premiums are typically much lower compared to permanent life insurance policies.
- No Cash Value: Unlike other life insurance policies, term life insurance does not build cash value over time. You simply pay for the death benefit during the term of the policy.
- Expiration: Once the term ends, the policyholder no longer has coverage unless they renew or convert the policy. However, renewals typically come with higher premiums due to age and health factors.
Who Should Consider Term Life Insurance?
Term life insurance is ideal for people who need temporary coverage for a specific period of time, such as when raising children or paying off a mortgage. It’s especially suited for young families or individuals seeking affordable protection with large death benefits.
2. Whole Life Insurance
Whole life insurance is a form of permanent life insurance, meaning it provides coverage for the entirety of the policyholder’s life, as long as premiums are paid. In addition to offering a death benefit, whole life insurance also includes a cash value component, which accumulates over time.
Key Features:
- Lifetime Coverage: As long as the policyholder continues to pay premiums, their beneficiaries will receive a death benefit whenever they pass away.
- Cash Value Accumulation: Unlike term life insurance, whole life policies accumulate cash value. This cash value grows at a guaranteed rate over time and can be accessed by the policyholder during their lifetime, either through loans or withdrawals.
- Fixed Premiums: Whole life insurance policies often come with fixed premiums, meaning the amount you pay stays the same throughout the life of the policy.
Advantages of Cash Value:
The cash value component can be especially helpful as it acts as a form of savings that grows tax-deferred. It can be used to supplement retirement income, pay for unexpected expenses, or even help with policy premiums if the cash value grows large enough.
Who Should Consider Whole Life Insurance?
Whole life insurance is best for individuals who are looking for lifelong protection and are interested in building savings over time. It’s often suited for people who want the predictability of fixed premiums and the ability to access cash value if needed. However, it’s important to note that whole life policies are more expensive than term life insurance.
3. Universal Life Insurance
Universal life insurance is another form of permanent life insurance that offers more flexibility than whole life policies. Like whole life, it provides lifetime coverage and includes a cash value component. However, universal life insurance allows policyholders to adjust their premiums and death benefit amounts over time, depending on their changing needs and financial situation.
Key Features:
- Flexible Premiums: Universal life insurance policies give policyholders the ability to adjust their premium payments. For example, you can pay higher premiums to grow the policy’s cash value faster or reduce premiums during tough financial times, as long as there is enough cash value to cover the cost of insurance.
- Cash Value Accumulation: Like whole life, universal life policies accumulate cash value that grows tax-deferred. However, the rate of return on the cash value can vary, often based on prevailing interest rates or other financial factors.
- Potential for Higher Returns: Universal life policies often have the potential to earn a higher return on the cash value than whole life policies, depending on market conditions.
Who Should Consider Universal Life Insurance?
Universal life insurance is a good fit for individuals who want lifelong coverage but also need flexibility in premium payments and death benefit options. It’s well-suited for people with fluctuating incomes or those who want more control over how their policy evolves.
4. Variable Life Insurance
Variable life insurance combines the lifelong coverage of whole life insurance with an investment component. While it shares similarities with whole life policies, variable life allows policyholders to invest the cash value in a range of investment options, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds.
Key Features:
- Investment Opportunities: The cash value in a variable life insurance policy is tied to investment portfolios. This offers the potential for higher returns compared to whole or universal life policies, but also comes with the risk of losing cash value if the investments perform poorly.
- No Guaranteed Cash Value: Unlike whole or universal life insurance, variable life insurance does not guarantee a minimum cash value. If the chosen investments perform well, the cash value and death benefit can grow significantly. However, if they perform poorly, the cash value can decrease, and in extreme cases, the death benefit may be impacted.
- Fixed Premiums: Despite the variability of the cash value, premiums in a variable life policy are typically fixed, providing some stability.
Who Should Consider Variable Life Insurance?
Variable life insurance is suited for individuals who are comfortable with investment risk and want the potential for higher cash value growth. This type of policy is ideal for those who have an interest in managing their investment portfolio and are financially secure enough to weather market fluctuations.
How to Choose the Right Life Insurance Policy
Choosing the right life insurance policy depends on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and the needs of your dependents. Here are a few factors to consider:
- Budget: Term life insurance is typically the most affordable option, especially for young families or individuals with tight budgets. Whole life and universal life policies are more expensive but provide lifelong coverage and cash value accumulation.
- Coverage Period: If you only need coverage for a specific period (e.g., while paying off a mortgage or raising children), term life insurance may be the best choice. If you want lifelong protection, whole life, universal life, or variable life insurance are better options.
- Investment Goals: If you’re interested in a policy that grows in value and offers investment opportunities, universal life or variable life insurance may be appealing. However, they come with added risk and complexity, so it’s important to fully understand the investment component.
- Flexibility: If your financial situation changes frequently or you expect it to, a universal life policy may be a good option due to its flexibility with premium payments and death benefits.
Conclusion
Life insurance is a crucial part of financial planning, but the variety of options can be overwhelming. Understanding the differences between term life, whole life, universal life, and variable life insurance can help you make the best choice for your personal and financial circumstances. Whether you’re looking for affordable temporary coverage or a lifelong policy that builds savings, there’s a life insurance product designed to meet your needs.
Taking the time to evaluate your financial goals and consult with a financial advisor will help ensure that you choose the right policy for you and your loved ones.